Difference between revisions of "GVBuffer"
(→Structure) |
m (→Structure) |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | The | + | The {{GVBUFFER}} data structure (it.greenvulcano.gvesb.buffer.GVBuffer) represents the container that carries information within the components of {{GVESB}}: |
| − | + | ||
| − | The business information | + | Inbound Adapter <-> Core <-> Plug-in outbound |
| − | The data structure contains properties specific of | + | |
| − | *Service: service invoked | + | The business information are inserted in the 'object' field, the {{GVBUFFER}} data structure can contains any data type: JMS messages, SOAP Envelope, Document, strings, byte arrays, etc. |
| − | *System: the system client identifier that invokes the service | + | The data structure contains properties specific of {{GVESB}} platform: |
| − | *Id: the identifier of the particular transaction (eg, to identify the response of a specific asynchronous request) | + | *[[Service|service]]: service invoked |
| − | * | + | *[[System|system]]: the system client identifier that invokes the service |
| − | + | *[[Id|id]]: the identifier of the particular transaction (eg, to identify the response of a specific asynchronous request), the id is unique for the all service execution | |
| + | *retCode: return code of the service invocation (possibly defined by the client/server contract for a specific service) | ||
| + | The data structure also offers the ability to define and modify some service specific properties within the workflow, to be used by JavaScript and/or OGNL and in evaluating routing conditions. | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | [[File:GVBuffer.png|thumb| | + | [[File:GVBuffer.png|thumb|GVBuffer structure]] |
| − | |||
| − | *Platform fields, | + | All {{GVBUFFER}}s have the same shape, based on three primary components (see the image): |
| + | *Platform fields, those fields contain all information to indentify the flow | ||
*Properties, this section contains an object thats maps keys to values. This object cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. | *Properties, this section contains an object thats maps keys to values. This object cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. | ||
| − | *Payload, This buffer section contains | + | *Payload, This buffer section contains the service data |
| − | + | A single service can have more {{GVBUFFER}} instances in its [[Execution Context]], each operation (node) in a {{GVESB}} service can declare a {{GVBUFFER}} as input and/or output. A {{GVBUFFER}} in the [[Execution Context]] can be also overwritten by another operation. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Following the {{GVBUFFER}} public fields/methods: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java5"> | ||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Constructs a GVBuffer with all fields. | ||
| + | * @throws GVException if system or service or id are null | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public GVBuffer(String system, String service, Id id, int retCode, Object object) throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Construct a GVBuffer with system, service, id. | ||
| + | * @throws GVException if system or service or id are null | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public GVBuffer(String system, String service, Id id) throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Construct a GVBuffer with system and service. | ||
| + | * @throws GVException if system or service are null | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public GVBuffer(String system, String service) throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Default constructor. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public GVBuffer() throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Copy constructor. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public GVBuffer(GVBuffer toCopy) | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the system | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public String getSystem() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the service | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public String getService() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the id | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public Id getId() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the retCode | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public int getRetCode() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the internal object | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public Object getObject() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param system | ||
| + | * @throws GVException if system is null | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void setSystem(String system) throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param service | ||
| + | * @throws GVException if service is null | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void setService(String service) throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param id | ||
| + | * @throws GVException if id is null | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void setId(Id id) throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param retCode | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void setRetCode(int retCode) | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param object | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void setObject(Object object) | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return properties. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | private Map<String, String> getProperties() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param name | ||
| + | * @return the property value | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public String getProperty(String name) | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the property names iterator | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public Iterator<String> getPropertyNamesIterator() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the property names set | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public Set<String> getPropertyNamesSet() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @return the property names as array of string | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public String[] getPropertyNames() | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param property | ||
| + | * @param value | ||
| + | * @throws GVException if name or value are null | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void setProperty(String property, String value) throws GVException | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param property | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void removeProperty(String property) | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * @param props | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public void removeProperties(Map<String, String> props) | ||
| + | |||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
====Example==== | ====Example==== | ||
| − | In the example below is shown a flow composed of | + | In the example below is shown a flow composed of four nodes. The first one uses as input {{GVBUFFER}} associated to the identifier 'to_process'; the result of the node processing will be into another {{GVBUFFER}} associated to the 'read_data' identifier. Subsequent nodes will work on the same buffer ('read_data'), which will be the output parameter of the <GVEndNode>: so information in it will be delivered to the client. |
<syntaxhighlight lang="XML"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="XML"> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 159: | ||
id-system="CREDIT" input="to_process" | id-system="CREDIT" input="to_process" | ||
next-node-id="add_ext" op-type="call" | next-node-id="add_ext" op-type="call" | ||
| − | operation-name="CreditCards" output=" | + | operation-name="CreditCards" output="read_data" |
point-x="149" point-y="140" type="flow-node"/> | point-x="149" point-y="140" type="flow-node"/> | ||
<ChangeGVBufferNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.ChangeGVBufferNode" | <ChangeGVBufferNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.ChangeGVBufferNode" | ||
| − | dump-in-out="false" id="add_ext" input=" | + | dump-in-out="false" id="add_ext" input="read_data" |
next-node-id="send_email" | next-node-id="send_email" | ||
op-type="change GVBuffer" point-x="309" | op-type="change GVBuffer" point-x="309" | ||
| Line 44: | Line 173: | ||
<GVOperationNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.GVOperationNode" | <GVOperationNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.GVOperationNode" | ||
dump-in-out="false" id="send_email" | dump-in-out="false" id="send_email" | ||
| − | id-system="CREDIT" input=" | + | id-system="CREDIT" input="read_data" |
next-node-id="end" op-type="call" | next-node-id="end" op-type="call" | ||
operation-name="SendEmailSVCResponse" | operation-name="SendEmailSVCResponse" | ||
| − | output=" | + | output="read_data" point-x="473" point-y="137" |
type="flow-node"/> | type="flow-node"/> | ||
<GVEndNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.GVEndNode" | <GVEndNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.GVEndNode" | ||
end-business-process="yes" id="end" op-type="end" | end-business-process="yes" id="end" op-type="end" | ||
| − | output=" | + | output="read_data" point-x="671" point-y="137" |
type="flow-node"> | type="flow-node"> | ||
<ChangeGVBuffer clear-data="true"/> | <ChangeGVBuffer clear-data="true"/> | ||
</GVEndNode> | </GVEndNode> | ||
</Flow> | </Flow> | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Example of {{GVBUFFER}} manipulation through JavaScript: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="javascript"> | ||
| + | // data is a GVBuffer instance | ||
| + | |||
| + | // suppose data.object contains a java.lang.String | ||
| + | var obj = data.getObject(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // set a service specific property | ||
| + | data.setProperty("STR_LENGTH", obj.length()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // set a platform property | ||
| + | data.setRetCode(-1000); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // modify the payload | ||
| + | data.setObject(obj.getBytes()); | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The same example built with OGNL. | ||
| + | The comments aren't allowed in OGNL scripts, so are defined externally: | ||
| + | <nowiki>#</nowiki>input is a GVBuffer instance, suppose <nowiki>#</nowiki>input.object contains a java.lang.String, then set a service specific property, and finally set a platform property | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="javascript"> | ||
| + | #obj = #input.object, | ||
| + | #input.property['STR_LENGTH'] = #obj.length(), | ||
| + | #input.retCode = -1000 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:06, 14 February 2012
Description
The GVBuffer data structure (it.greenvulcano.gvesb.buffer.GVBuffer) represents the container that carries information within the components of GreenVulcano® ESB:
Inbound Adapter <-> Core <-> Plug-in outbound
The business information are inserted in the 'object' field, the GVBuffer data structure can contains any data type: JMS messages, SOAP Envelope, Document, strings, byte arrays, etc. The data structure contains properties specific of GreenVulcano® ESB platform:
- service: service invoked
- system: the system client identifier that invokes the service
- id: the identifier of the particular transaction (eg, to identify the response of a specific asynchronous request), the id is unique for the all service execution
- retCode: return code of the service invocation (possibly defined by the client/server contract for a specific service)
The data structure also offers the ability to define and modify some service specific properties within the workflow, to be used by JavaScript and/or OGNL and in evaluating routing conditions.
Structure
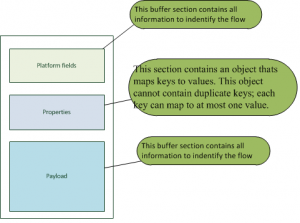
All GVBuffers have the same shape, based on three primary components (see the image):
- Platform fields, those fields contain all information to indentify the flow
- Properties, this section contains an object thats maps keys to values. This object cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value.
- Payload, This buffer section contains the service data
A single service can have more GVBuffer instances in its Execution Context, each operation (node) in a GreenVulcano® ESB service can declare a GVBuffer as input and/or output. A GVBuffer in the Execution Context can be also overwritten by another operation.
Following the GVBuffer public fields/methods:
/**
* Constructs a GVBuffer with all fields.
* @throws GVException if system or service or id are null
*/
public GVBuffer(String system, String service, Id id, int retCode, Object object) throws GVException
/**
* Construct a GVBuffer with system, service, id.
* @throws GVException if system or service or id are null
*/
public GVBuffer(String system, String service, Id id) throws GVException
/**
* Construct a GVBuffer with system and service.
* @throws GVException if system or service are null
*/
public GVBuffer(String system, String service) throws GVException
/**
* Default constructor.
*/
public GVBuffer() throws GVException
/**
* Copy constructor.
*/
public GVBuffer(GVBuffer toCopy)
/**
* @return the system
*/
public String getSystem()
/**
* @return the service
*/
public String getService()
/**
* @return the id
*/
public Id getId()
/**
* @return the retCode
*/
public int getRetCode()
/**
* @return the internal object
*/
public Object getObject()
/**
* @param system
* @throws GVException if system is null
*/
public void setSystem(String system) throws GVException
/**
* @param service
* @throws GVException if service is null
*/
public void setService(String service) throws GVException
/**
* @param id
* @throws GVException if id is null
*/
public void setId(Id id) throws GVException
/**
* @param retCode
*/
public void setRetCode(int retCode)
/**
* @param object
*/
public void setObject(Object object)
/**
* @return properties.
*/
private Map<String, String> getProperties()
/**
* @param name
* @return the property value
*/
public String getProperty(String name)
/**
* @return the property names iterator
*/
public Iterator<String> getPropertyNamesIterator()
/**
* @return the property names set
*/
public Set<String> getPropertyNamesSet()
/**
* @return the property names as array of string
*/
public String[] getPropertyNames()
/**
* @param property
* @param value
* @throws GVException if name or value are null
*/
public void setProperty(String property, String value) throws GVException
/**
* @param property
*/
public void removeProperty(String property)
/**
* @param props
*/
public void removeProperties(Map<String, String> props)
Example
In the example below is shown a flow composed of four nodes. The first one uses as input GVBuffer associated to the identifier 'to_process'; the result of the node processing will be into another GVBuffer associated to the 'read_data' identifier. Subsequent nodes will work on the same buffer ('read_data'), which will be the output parameter of the <GVEndNode>: so information in it will be delivered to the client.
<Flow first-node="extract_data" point-x="19" point-y="137">
<GVOperationNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.GVOperationNode"
dump-in-out="false" id="extract_data"
id-system="CREDIT" input="to_process"
next-node-id="add_ext" op-type="call"
operation-name="CreditCards" output="read_data"
point-x="149" point-y="140" type="flow-node"/>
<ChangeGVBufferNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.ChangeGVBufferNode"
dump-in-out="false" id="add_ext" input="read_data"
next-node-id="send_email"
op-type="change GVBuffer" point-x="309"
point-y="137" type="flow-node">
<ChangeGVBuffer clear-data="false">
<PropertyDef name="FILE_EXT"
value="decode{{ognl{{property['BIRT_REPORT_TYPE']}}::excel::xls::pdf}}"/>
</ChangeGVBuffer>
</ChangeGVBufferNode>
<GVOperationNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.GVOperationNode"
dump-in-out="false" id="send_email"
id-system="CREDIT" input="read_data"
next-node-id="end" op-type="call"
operation-name="SendEmailSVCResponse"
output="read_data" point-x="473" point-y="137"
type="flow-node"/>
<GVEndNode class="it.greenvulcano.gvesb.core.flow.GVEndNode"
end-business-process="yes" id="end" op-type="end"
output="read_data" point-x="671" point-y="137"
type="flow-node">
<ChangeGVBuffer clear-data="true"/>
</GVEndNode>
</Flow>
Example of GVBuffer manipulation through JavaScript:
// data is a GVBuffer instance
// suppose data.object contains a java.lang.String
var obj = data.getObject();
// set a service specific property
data.setProperty("STR_LENGTH", obj.length());
// set a platform property
data.setRetCode(-1000);
// modify the payload
data.setObject(obj.getBytes());
The same example built with OGNL. The comments aren't allowed in OGNL scripts, so are defined externally: #input is a GVBuffer instance, suppose #input.object contains a java.lang.String, then set a service specific property, and finally set a platform property
#obj = #input.object,
#input.property['STR_LENGTH'] = #obj.length(),
#input.retCode = -1000