GVExample TOUPPER
Description
This example shows a synchronous service.
How To
As this is our first example, the first step will be the creation of a new VulCon Project.
- From the Menu panel of VulCon click File -> New -> Project. A new windows will be open containing the projects type.
- Select "New Vulcon Project" item. Then click Next
- Set the project name and Location. We named the project as TEST and the Location as /home/user/Lavoro/GvEnterprise3.2.0/workflow. Then click finish. The new VulCon project TEST has been created.
The best mode for creating a Service is through the Wizard. But for use it you must first define the System, Channel and the operations you need for. From the core view:
- Expand the GVSystems item.
- Right clicking on Systems, insert-after -> System. A new element System will be created.
- Set the System parameters in the Properties panel. We named it GVESB_TEST
- By right clicking the System element, you can insert a new Channel.
- Click on this new Channel element and set the property id_channel. We named TEST_CHANNEL
- Finally, insert the operation you need for the workflow. In this case a test-service-call. Right clicking Channel -> Insert after (or Insert before) -> test-service-call. A new element will be created.
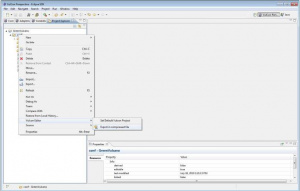
- Set the test-service-call attributes. From the properties view set those as follows:
- name: test.
Now we are able to use the Wizard.
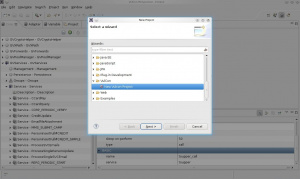
- From the Core View of VulCon. Right click the element Services -> Wizard New Service
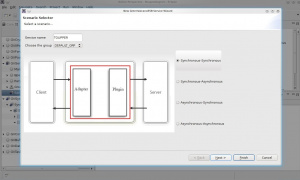
- A new windows will be open where you can set the name of the Service you want to create, in this case we named TOUPPER. You can also select the paradigm, for this example will be synchronous-synchronous. Click next.
- Set System as GVESB and Channel TEST_CHANNEL. Then finish.
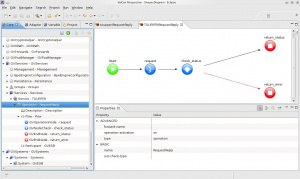
A new Service named TOUPPER has been created and the editor will be open automatically, showing the nodes involved in our Flow.
- The Start node sets the flow first node. In this case request
- The Operation node request calls the test-service-call operation test and executes it.
- A Check node named check_status is also inserted for controlling the success of the preceding node.
- If success flow passes to the End node return_status
- In case of Error, flow goes to the End node return_error. The difference with return_status is signed by the Connection with check_status Check node. In this case an Error Connection (the Red arrow) have been used.
- Save clicking the Save icon from the Core View
Now you are able to test your first VulCon service from the GV Console®. But first you need to export the configuration.
Once the flow is correctly configured, the user can export the configuration and pass it to the GreenVulcano® ESB import tool, in order to add into the ESB the service just created.
- The Export function is available in the view "Project". Expand the project
- Before you proceed press F5 to refresh the file list.
- Right click the conf folder. It will open a drop-down list.
- Clicking "Export" will be open a window. Select Vulcon Export Tool -> Vulcon Project. Then Next
- Select the project and set the path where you want to save the file. Then Finish
For knowing how test your service using GV Console® click here.