Difference between revisions of "XML Data mapper"
(→Links) |
(→Functions) |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
| [[XSLHelper | JavaScriptRetriever]] || execute JavaScript code | | [[XSLHelper | JavaScriptRetriever]] || execute JavaScript code | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can assign a constant value parameter of a function between right-clicking the mouse on the parameter | ||
===Additional nodes=== | ===Additional nodes=== | ||
Revision as of 09:27, 24 May 2012
Contents
Introduction
XML Data mapper module allows users to design a XSL data transformation from one XML document, defined by a source xsd, to another XML document, defined by a target xsd. The designer output is a XSL document associated to a data transformation defined in VulCon. The use of a graphical designer speeds up the process of defining the data mapping, and gives it a simple and efficient graphical representation.
Create a data transformation
The steps required to create a graphical data transformation are:
- Verify that the XSD documents describing the source/target XMLs are present in the /conf/xsds folder
- Access the VulCon Core view and expand the GVDataTransformation node
- Click on Transformations item with right mouse button and choose in the drop-down list
Transformations --> Create XSLT Transformation
- Populate the wizard parameters:
- Transformation Name: the name by which the transformation is referenced by GreenVulcano® ESB Core. Is also the name of the editor configuration file with .gvxdt extension and of the XSL transformation file with .xsl extension
- Data Source: the data source name that indicates the DTE repository where files will be created
- Path XSL: sub-folders of the selected data source path in which the XSL file will be generated
- XSD Input: XSD file name defining the source document. The files suggested by the drop-down list must be stored in the /conf/xsds folder
- root XSD Input: root element of the source XML document from which start the data transformation operation
- XSD Output: XSD file name defining the target document. The files suggested by the drop-down list must be stored in the /conf/xsds folder
- root XSD Output: root element of the target XML document
- Click the Finish button: in Graphic Editor VulCon perspective will appear the Data mapper graphic editor in which in possible to design the transformation
- Generate the resultant XSL file.
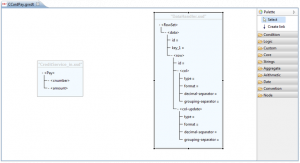
Data mapper graphic editor
In Data mapper graphic editor are visible the representations for input and output formats.Items followed by '=' character are attributes, while those enclosed in angle brackets '<>' are nodes of the XML document. Is it possible to collaps or expand child nodes simply by clicking on '+' or '-' symbols on the left of each node name. The right panel contains the palettes used for the definition of the data mapping functions. The Select button allows the selection of the xsd nodes interested for the transformation. The Create link button allows to define links:
- between a source and a target element;
- between a source element and a parameter of a function;
- between the output of a function and a parameter of another function;
- between the output of a function and a target element.
In the folders below that buttons, it is possible to access the functions used for data-mapping grouped by topic.
Open editor
To open the editor you can:
- double click a .gvxdt file previously created in the Project view;
- right-clicking on the XSLTransformation in the core view and then choosing the 'Open mapping <transformation name>' item.
Links
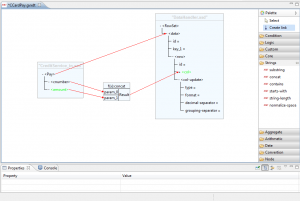
A link is a relation between the node in the source format and its counterpart in the target format. Clicking the Create link button in the Palette pane, link mode is enabled. In this mode is possible to create new connection simply clicking on a node in the XSD source model, and dragging it on a target node. Once defined a new connection in the graphic area, its properties are shown in Properties area. 'Match' property allows the definition of the selected mapping generation mode:
- template: a template node will be created, activated by the source element
- for-each: a for-each node will be created to process iteratively the source element
Other Properties:
- mode: allow an element to be processed multiple times, each time producing a different result.
- condition: boolean condition applied to template, condition is a drop list of all the condition that have been defined in the transformation
- priority: priority of a template rule is specified by the priority attribute on the template rule.
To add a node to the mapping must click the right mouse button on the main node.
Functions
Folders on the right of Graphic Editor contains the most common used XSLT and XPath functions, organized by topic.
To use a function is sufficient to select it in the appropriate folder and then to click in the design area. For those functions which have a variable number of parameters, such as the 'concat' function, a dedicated pop-up will open. Once done this steps, a graphical representation of the new function will be shown in the design area.
At this point you need to create all links to map the input parameters and the one to define the element that will assume the output value of the function.
To give a constant value to a function parameter you must right-click on its graphical representation and then insert the value. To modify a parameter value simply set it in the corresponding property in the lower Property editor.
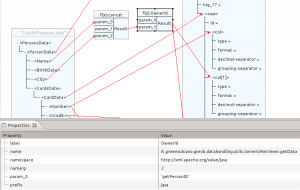
If the desired function is not present inside function folders, it is possible to define it choosing from Custom folder. To do this you must enter values in the following fields:
- Name: the name of the function to create (eg.: java:it.greenvulcano.gvesb.datahandling.utils.GenericRetriever.getData).
- Label: the label displayed on the editor (eg.: getId).
- Numarg: the number of function arguments.
- Prefix: the namespace prefix used by the function (example: java).
- Namespace: the namespace of the function (eg.: http://xml.apache.org/xalan/java)
The following table presents some XSL helper classes, useful in XSL data manipulation:
| Helper | Use this for ... |
|---|---|
| XSLTUtils | manipulate date/time and strings |
| GenericRetriever | query the database for data conversion |
| JavaScriptRetriever | execute JavaScript code |
You can assign a constant value parameter of a function between right-clicking the mouse on the parameter
Additional nodes
Some XSL transformations need to create nodes by duplicating the base node. To realize this operation, simply select the base node with the right mouse button and then a new duplicate node will be created. An ordinal value will be reported next to the new selected node. A node with an 'n' ordinal value represents the only n-th instance of that node. A node without ordinal values represents all the nodes of that type.
Xsl file generation
To generate the xsl file you must select the 'xsl Save File' menu item icon on the editor tool bar. The file will be created in the subsequently selected directory.